The Non-Ionizing Radiation Safety Program is designed to help protect University personnel, students and the general public from the harmful effects of non-ionizing radiation.
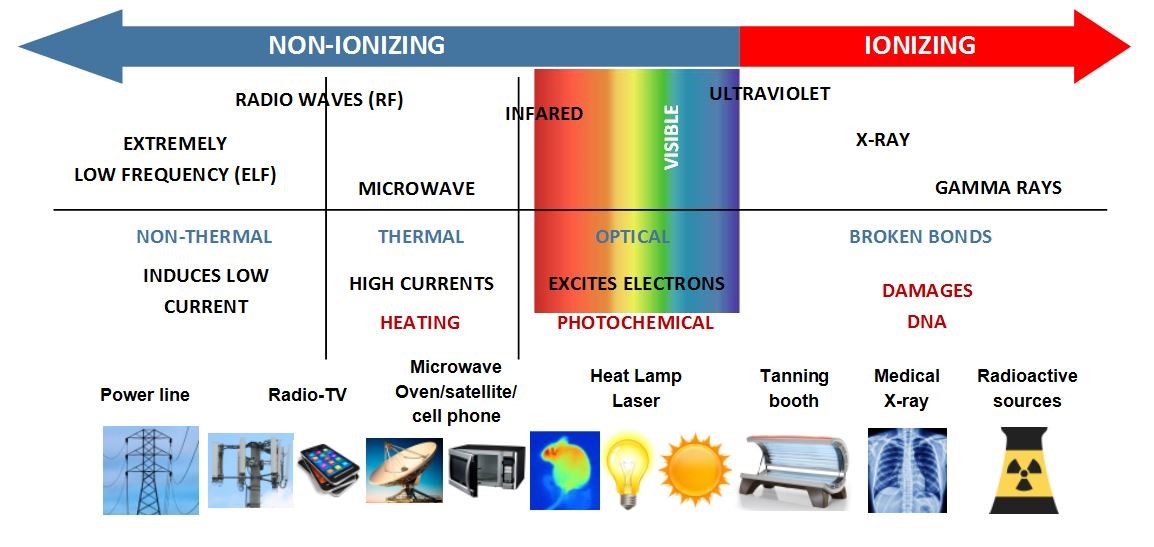
Non-ionizing radiation (NIR) refers to electromagnetic radiation that does not have sufficient energy to ionize (remove electrons from) atoms or molecules. Instead, the energy is converted to heat, which can lead to burns, depending on the exposure time, wavelength/frequency, and the energy concentration of the radiation. NIR sources can pose a human health hazard; therefore, individuals working with non-ionizing radiation should take precautions to avoid excessive exposure.
Non-ionizing radiation at the UW
There are many sources of non-ionizing radiation within the University such as nuclear magnetic resonance, magnetic resonance imaging, nuclear fusion research, furnaces, microwave ovens, UV lamps, fluorescent objects, induction heaters, transmission generators, Wi-Fi, mobile phones, cell antennas and more. These sources produce NIR in the electromagnetic spectrum of wavelengths/frequencies ranging from 100 nm to static fields.
Sources of non-ionizing radiation that pose a risk are generally associated with a specific research project or only pose a risk during maintenance activities when existing controls are removed or modified.
Refer to the sections below and the Non-Ionizing Radiation (NIR) Safety Manual for guidance in maintaining a safe work environment when using non-ionizing radiation.
Types of non-ionizing radiation
Three broad categories of NIR electromagnetic spectrum are:
- Optical radiation (100 nm-1 mm) - ultraviolet (UV), visible and infrared
- Microwave radiation (300 GHz to 300 MHz)
- Radiofrequency and lower frequency radiation (300 MHz to Static Fields)
Laboratories using ultraviolet (UV) equipment (e.g., transilluminator, gel documentation equipment, biosafety cabinet, crosslinker or curing light) should be provided with the following personal protective equipment (PPE):
- Appropriately rated safety glasses, goggles, or face shields
- Long-sleeved clothing to protect arms, hands and neck
- Gloves
For more information, please see the UV Safety Focus Sheet and the Guide Protecting Workers from UV Radiation.
Microwave Ovens
Although it is uncommon for commercial microwave ovens to leak, misuse, damage, and interlock failures can result in leaks. If you suspect a microwave oven is leaking, please report it to EH&S Radiation Safety, and we will survey it upon request.
The following control measures or care must be taken while using microwaves:
- Do not use a metal stirrer or plastic-coated magnetic stirrer bars, aluminum foil wires, cables in a microwave oven.
- Do not attempt to heat flammable liquids or solids, hazardous substances or radioactive material in a microwave oven.
- Do not heat-sealed containers; pressure can build up can cause an explosion either in the oven or shortly after removal.
- Do not use plastic containers in a microwave oven.
- Do not overheat liquids in a microwave oven. It is possible to raise water to a temperature greater than the normal boiling point; when this occurs, any disturbance to the liquid can trigger violent boiling that could result in severe burns.
- No unauthorized repairs on a microwave oven. If a unit is suspected to be malfunctioning, disconnect it from the power supply, remove it from service and label it with an appropriate tag while awaiting repair or disposal. Any irreparable microwave oven should be rendered inoperable by removal of the plug and cord before disposal.
- If the door hinges, latch or seals are damaged, it is safer and cheaper to replace the entire unit.
Radiofrequency-generating devices at the UW are most commonly used for telecommunication purposes (e.g., radio, television, microwave, mobile phones, base stations, Wi-Fi, radio transmitters, or wireless antennas).
The operation of radio, television, microwave, and other communication systems using electromagnetic radiation, as well as carrier-current systems, requires prior review and approval by UW-IT and Environment, Health & Safety (EH&S). EH&S Radiation Safety will assist in identifying and assessing microwave/RF radiation hazards in your work area. Due to the challenges of conducting actual surveys (near-field measurements, equipment costs, etc.), calculations and computer models are often used instead of direct measurements to evaluate the hazard.
Antennas and Antenna Arrays
Wireless antennas, when active, produce radiofrequency (RF) radiation which is regulated by the Federal Communications Commission.
Wireless antennas (or RF emitters) have been installed across campus rooftops. These antennas display warning signs indicating restricted access and may necessitate RF Safety Awareness Training and authorization from EH&S Radiation Safety before entry. UW personnel working in an area where an antenna is installed are required to follow general and site-specific safe work practices.
Visit the Radiofrequency: Wireless Cellular Antennas page for safety information for University personnel who work in or near University locations where wireless cellular antennas are installed. For additional RF safety guidance or personal dosimeter, contact the Radiation Safety Office.
Static magnetic fields are created from a fixed magnet or magnetic flux resulting from the flow of electric current. The greater the current, the stronger the magnetic field. Instruments that generate large static magnetic fields such as nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometers and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners are commonly present in research laboratories.
Objects made of ferrous materials such as steel can become a projectile when it is pulled rapidly toward the strong magnet and result in a hazardous situation or injury. Therefore, objects such as keys, scissors, knives, wrenches, oxygen cylinders and other ferromagnetic objects must be prohibited from the immediate vicinity of the magnet. In addition, anyone wearing cardiac pacemakers, metallic implants, and other electronic or electromagnetic prosthetic devices should be kept away from strong electromagnetic sources.
Superconducting magnets use liquid nitrogen and liquid helium coolants, to maintain the magnet coils in their superconductive state. Hence, precautions associated with the use of such cryogenic liquids must be observed as well.
For more information, please see the Compressed Gas Cylinder Safety Guidelines, Safe Handling of Cryogenic Substances Focus Sheet and Superconducting Magnets: Basic Safety Focus Sheet.
Services available
EH&S provides the following services:
- Worker and ancillary worker safety training
- Hazard assessment of NIR sources
- Space design review
- Consultation on disability accommodations and electromagnetic interference (EMI) in the workplace.
Frequently asked question
Please refer to the Laser Safety page or contact the Radiation Safety Office for additional guidance.
More Information
Training specific to potential non-ionizing radiation hazards in your workplace is available through the Radiation Safety Office upon request.
Washington Administrative Code WAC 296-62-09005 Non-ionizing radiation.
Non-coherent UV, Visible, Infrared Radiation - American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH), ANSI Z136.2
Microwave/Radio Frequency Radiation - The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) OET 65, The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) C95.1, American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH)
Extremely Low-Frequency Radiation - The International Radiation Protection Association/International Non-Ionizing Radiation Committee (IRPA/INIRC) —NIR Protection Guidelines
Static Magnetic Fields - American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH)
Emergency response and reporting
UW personnel are required to submit an incident report to Environmental Health & Safety for any work-related event that results in an injury, illness, exposure to hazardous materials, property damage, or fire, regardless of the work location. UW personnel are highly encouraged to submit work-related near-miss events.
Visit the Incident Reporting page for more information.